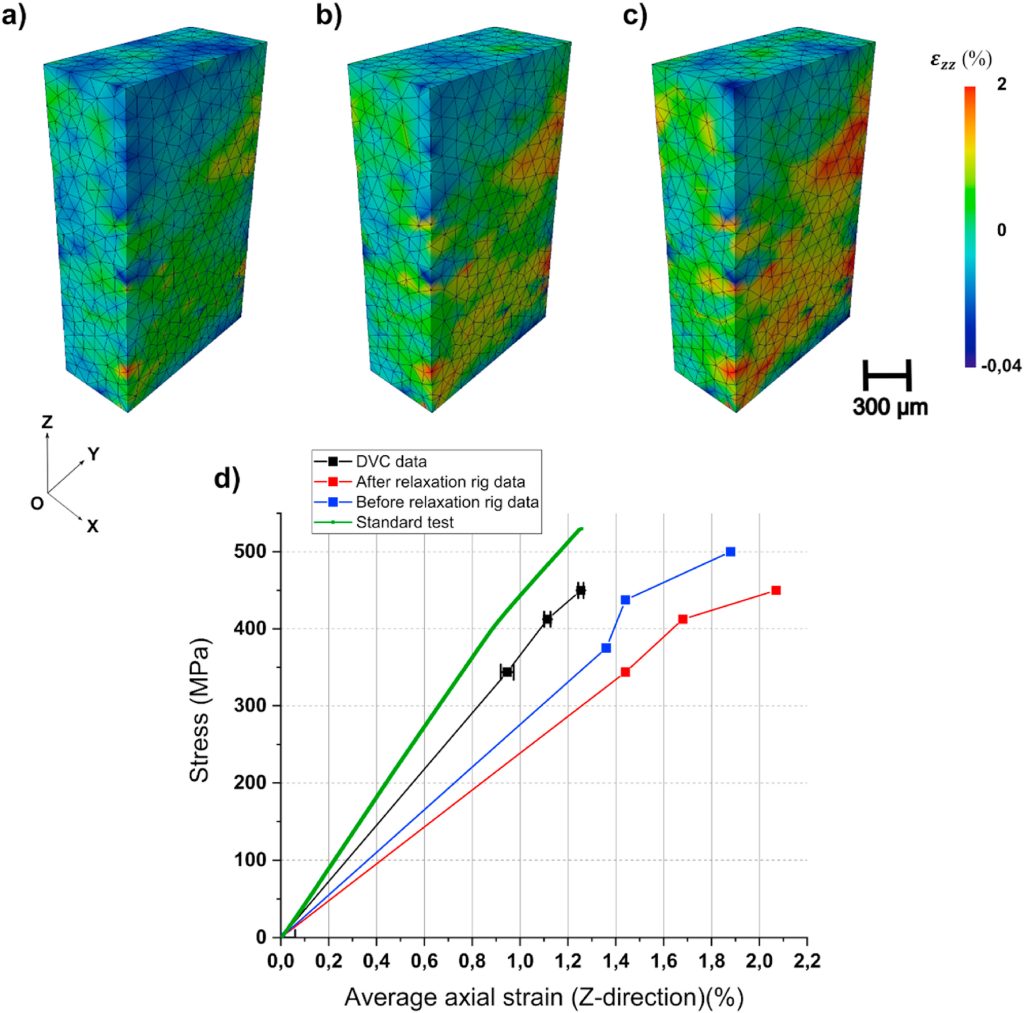
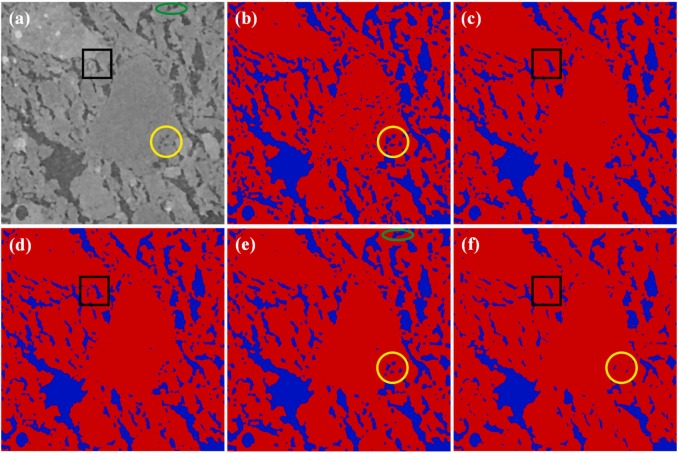
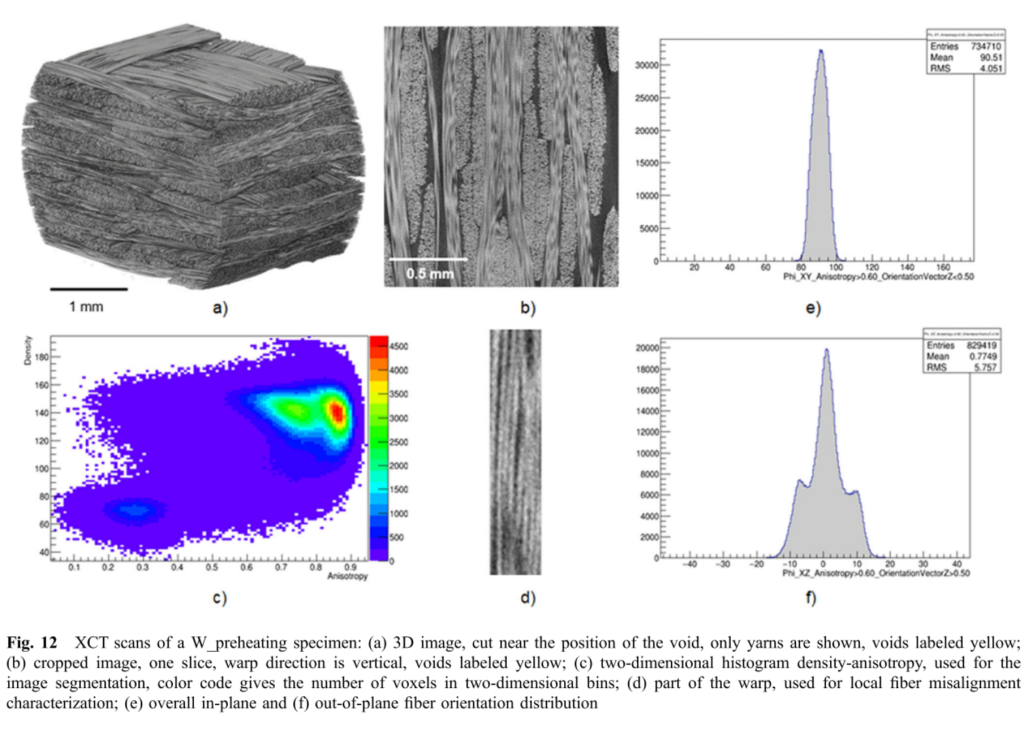
A time-resolved X-ray microcomputed tomography study of fermenting gluten-starch model doughs containing wheat and oat flour water extracts enriched in proteins
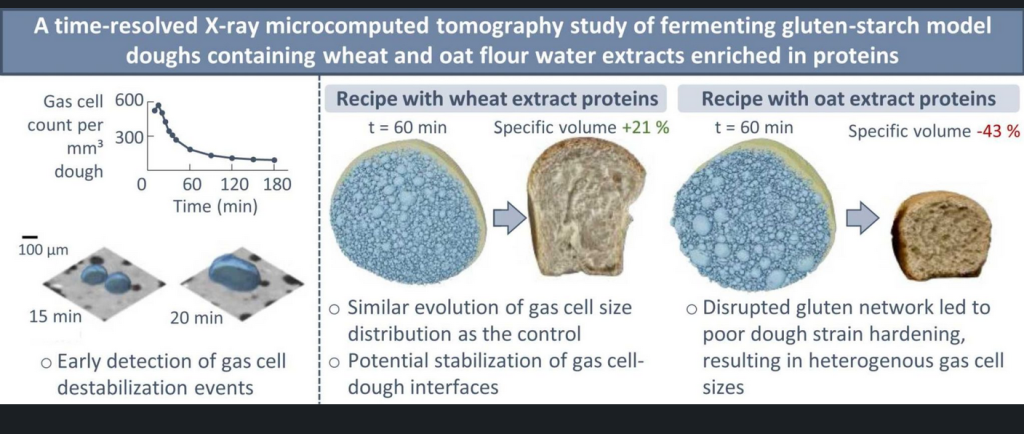
A B S T R A C T Water-extractable (WE) cereal flour constituents significantly influence bread loaf volume. However, the underlying mechanisms and the contribution of different constituents remain unclear. Here, time-resolved X-ray microcomputed tomography ( µ CT) and confocal laser scanning microscopy were utilized to study the impact of wheat and oat flour water […]