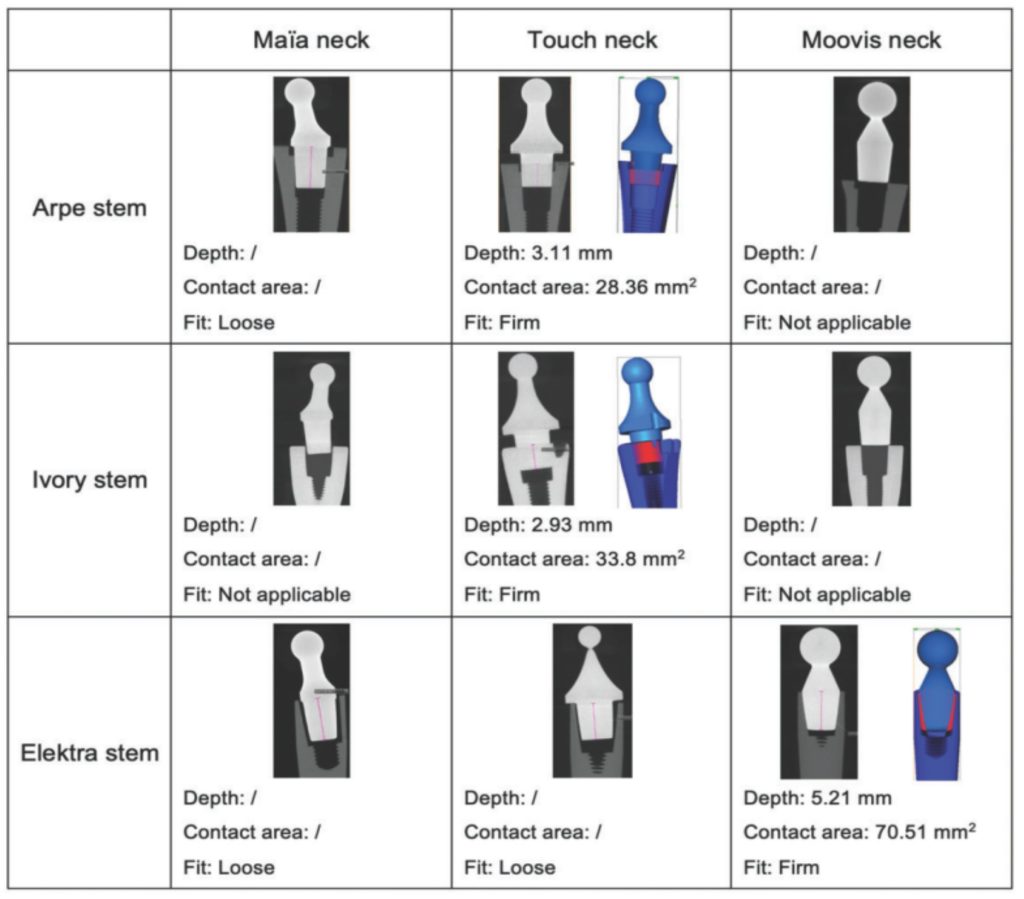
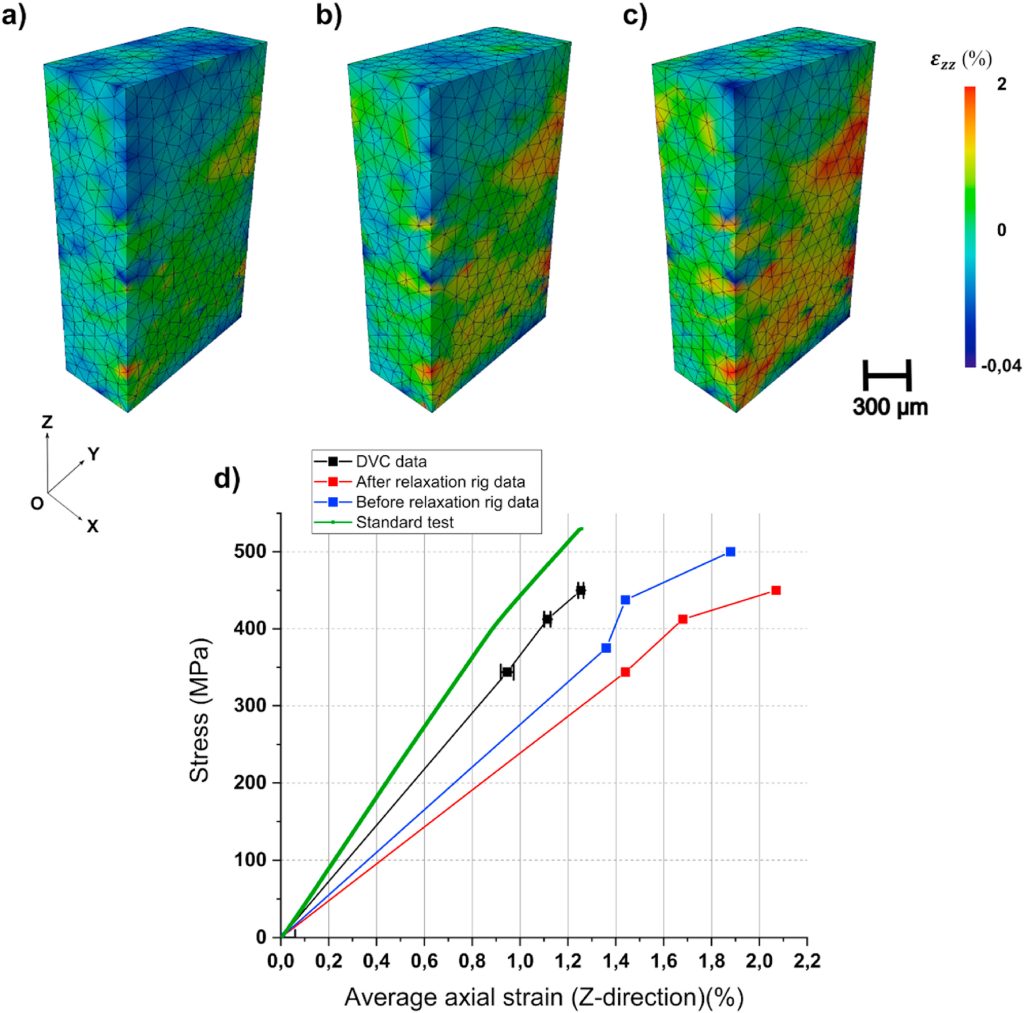
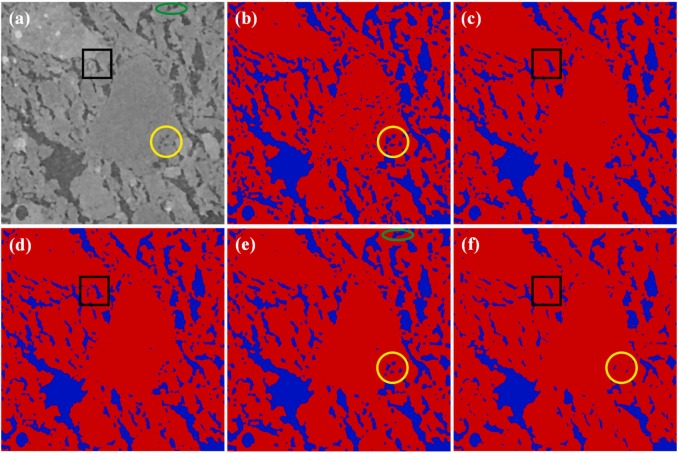
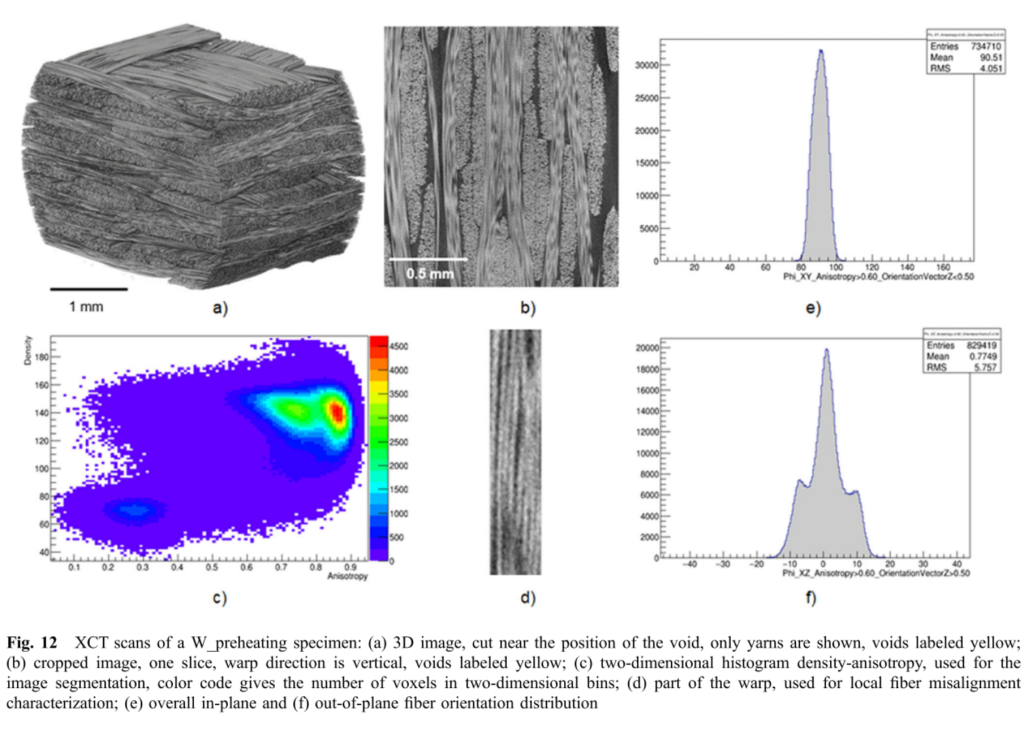
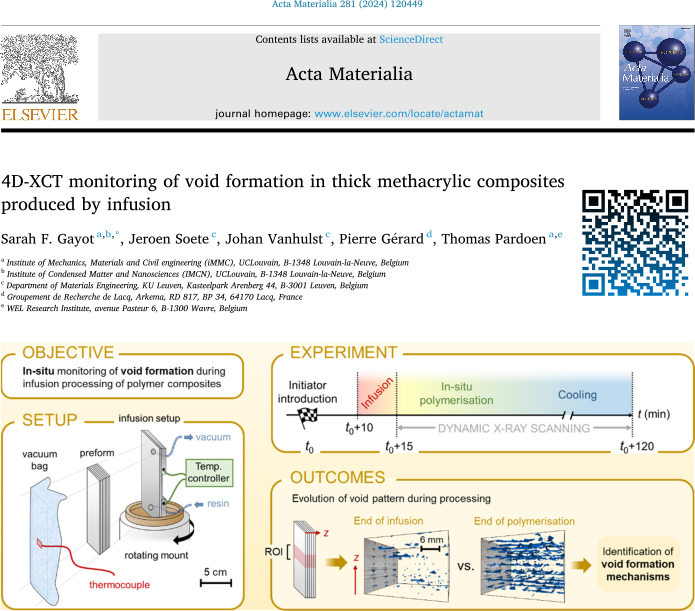
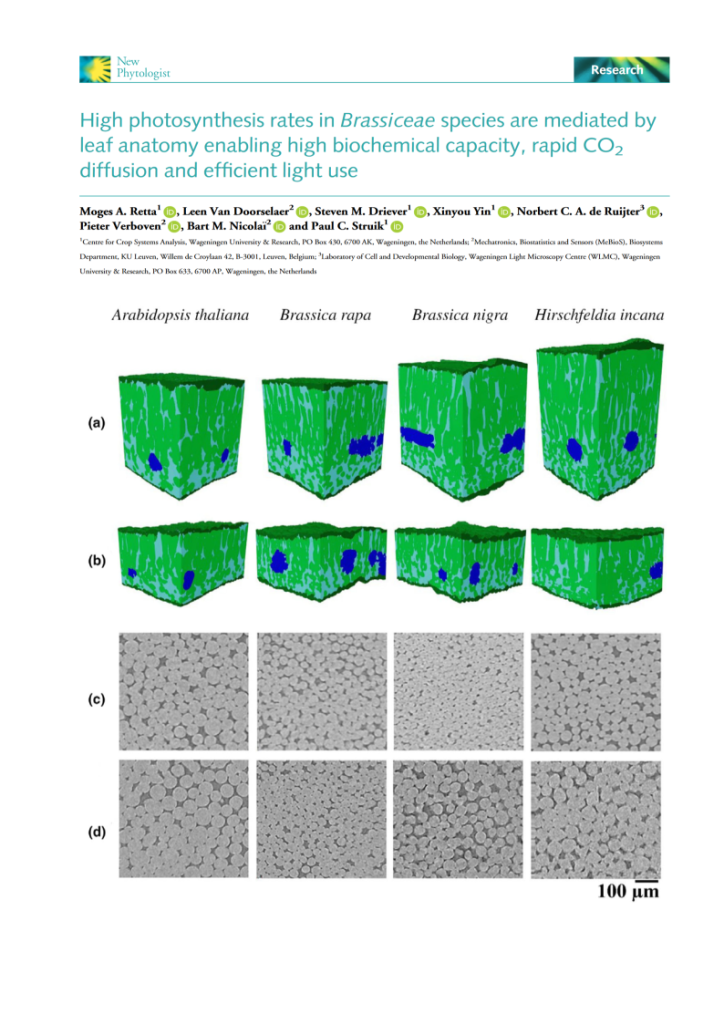
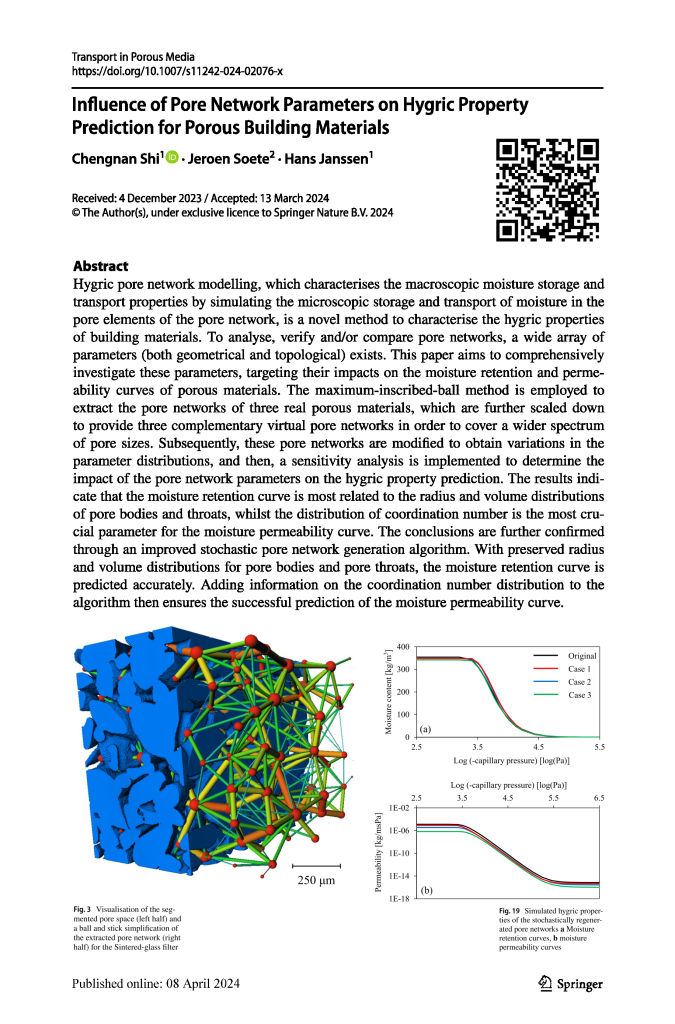
7th Symposium on X-ray Computed Tomography organized by the KU Leuven XCT Core Facility, to take place on May 6, 2025
Dear all, We are excited to announce the 7th Symposium on X-ray Computed Tomography organized by the KU Leuven XCT Core Facility, to take place on May 6, 2025 at the Thermotechnical Institute in Heverlee (KU Leuven). The symposium, presents an attractive program and stimulates networking, connecting researchers and industrial collaborators in the field. The […]