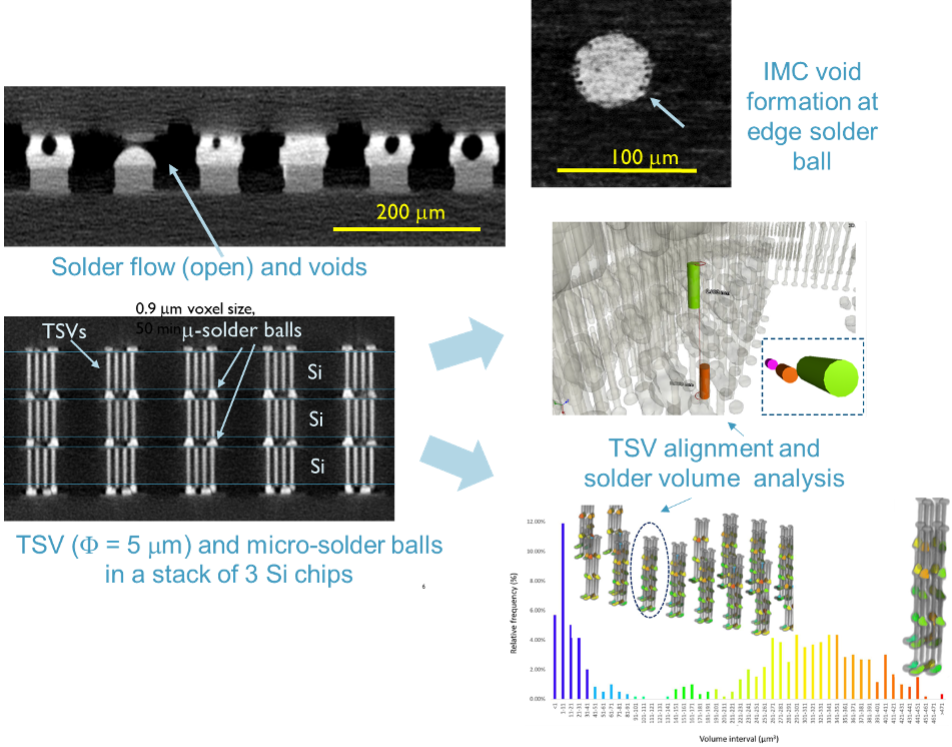
Micro-electronics (in collaboration with imec)
In the microelectronics industry, XCT is commonly used for failure analysis of chip packages and printed circuit bords (PCB). Imec (www.imec.be) investigates and develops innovative nano- and digital technologies. Some of these developments require non-destructive imaging of the internal structure. An important example is 3D-technology, but also development in other technologies, such as battery, optical […]
Micro-electronics (in collaboration with imec) Read More »